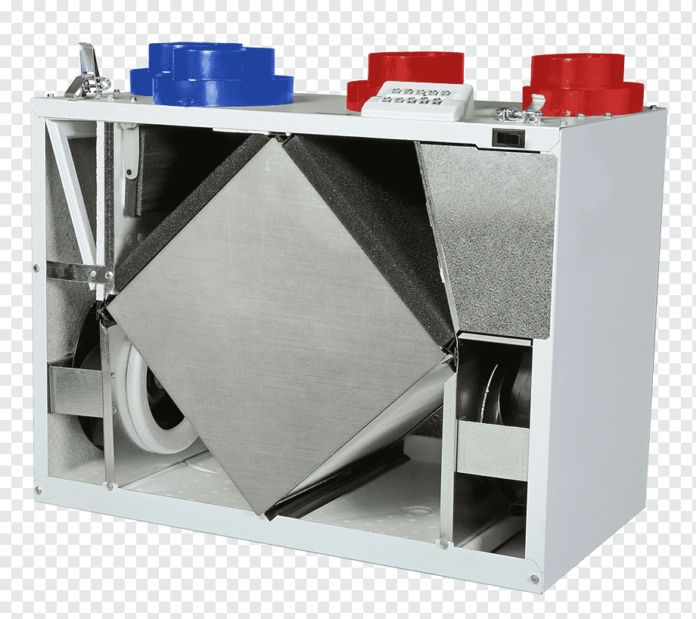
Energy consumption is a major concern in today’s world. As the demand for energy continues to rise, it is important to find ways to maximise efficiency and reduce waste. One solution to this challenge is the use of energy recovery heat exchanger. These innovative devices have been gaining popularity in various industries due to their ability to recover and reuse heat that would otherwise be lost. In simple terms, energy-recovery heat exchangers work by transferring thermal energy from one fluid or gas stream to another without allowing them to mix.
The Power of Energy-Recovery Heat Exchangers in Boosting Sustainability
Energy-Recovery Heat Exchangers serve as a cornerstone in advancing sustainability within various sectors. These systems underscore the shift towards more energy-conscious operations by capturing waste heat that would traditionally dissipate into the environment. The reclamation and subsequent utilisation of this heat is pivotal in diminishing the reliance on primary energy sources, often finite and environmentally taxing. By implementing Energy-Recovery Heat Exchangers, industries can witness a substantial reduction in energy requirements.
This conservation of energy translates to diminished greenhouse gas emissions, which are a major contributor to global warming and climate change. The process fosters a more sustainable operational model and aligns with the growing global mandate for eco-friendly practices. Furthermore, integrating these heat exchangers into existing systems underscores an innovative approach to waste management—transforming what is commonly seen as unusable heat into a valuable resource.
This paradigm shift is critical in achieving a lower carbon footprint across industry sectors. It propels the notion that sustainability and efficient energy use are not mutually exclusive but complementary components of modern industry. By embedding Energy-Recovery Heat Exchangers into the core of energy systems, a robust platform is created to promote environmental stewardship while advancing economic viability.
The Role of Home Air Heat Exchanger in Sustainable Development
In the realm of sustainable development, the incorporation of Home Air Heat Exchanger within residential environments plays a pivotal role. These innovative systems are engineered to enhance indoor air quality by facilitating the exchange of stale indoor air with fresh outdoor air, all while adeptly transferring heat between the two air streams. Such a mechanism not only aids in preserving a comfortable and healthy indoor climate but also substantially curtails the dependence on conventional heating and cooling systems.
Consequently, this leads to a marked reduction in energy consumption, aligning with broader environmental sustainability goals. Moreover, Home Air Heat Exchangers are instrumental in promoting energy conservation within the household, thereby contributing to the reduction of residential buildings’ overall carbon footprint. This energy conservation is of paramount importance in the current climate, where reducing energy usage is a critical component of global efforts to mitigate climate change.
The ability of these systems to maintain optimal indoor air conditions without the excessive use of energy-intensive appliances is a testament to their role in fostering sustainable living practices. Additionally, by diminishing the need for external heating or cooling sources, Home Air Heat Exchangers provide an eco-friendly solution that dovetails with sustainable development aspirations. They offer a greener alternative to traditional HVAC systems and underscore the potential for residential spaces to contribute to the broader environmental objectives of reducing energy usage and minimising greenhouse gas emissions.
Cost Savings Associated With Energy-Recovery Heat Exchangers
The financial implications of integrating Energy-Recovery Heat Exchangers into industrial and residential settings are profound, underscoring their value as a pivotal investment towards cost-efficiency and energy conservation. These systems leverage the principle of waste heat recovery, effectively minimising the need for additional energy to heat or cool spaces. This capability significantly reduces the energy demand on primary systems, thus translating into substantial savings on utility bills.
In the industrial sector, applying Energy-Recovery Heat Exchangers is a strategic move towards operational cost reduction. These systems feed the recovered energy back into the production cycle by recapturing heat from exhaust gases and other by-products of manufacturing processes. This recycling of energy not only slashes the consumption of new energy but lowers the operational expenses associated with heating and cooling requirements.
Residentially, adopting these heat exchangers brings about marked reductions in energy expenditure. Transferring heat from outgoing stale air to incoming fresh air ensures that indoor climate control is achieved more efficiently. This process reduces the dependency on conventional heating and cooling appliances, which are often significant contributors to household energy bills. Moreover, the investment in Energy-Recovery Heat Exchangers tends to pay dividends over time, with the reduction in energy costs outweighing the initial capital outlay required for their installation.
Applications of Heat Recovery Air Exchanger across Industries
Through their versatile functionality, Heat Recovery Air Exchanger has found a prominent place across a myriad of industries, serving to enhance operational efficiency and environmental sustainability. These systems are instrumental in optimising energy use within the HVAC sector by facilitating heat transfer between outgoing and incoming air streams. This ensures a balanced indoor climate and significantly reduces the load on heating and cooling systems, thus conserving energy.
In the industrial landscape, energy recovery heat exchangers are harnessed to recapture heat from exhaust gases and other by-products of manufacturing processes. The recovered heat is then fed back into the system, either for preheating raw materials or other thermal applications, curtailing the demand for additional energy sources. This cycle of energy reuse represents a leap towards more sustainable industrial operations, reducing energy consumption and operational costs.
Commercial buildings, with their substantial energy requirements for heating, ventilation, and air conditioning, benefit greatly from implementing these heat exchangers. By recovering waste heat from various sources within the building, such as the HVAC system itself or technological equipment, these establishments can achieve a notable decrease in energy usage. This lowers the carbon footprint associated with running large commercial spaces and translates into significant cost savings over time.
Enhancing Indoor Air Quality through Energy-Recovery Heat Exchangers
The critical role of Energy-Recovery Heat Exchangers in improving indoor air quality is increasingly recognised in contemporary health and environmental sustainability discussions. These systems, adept at exchanging stale indoor air with fresh outdoor air, are instrumental in eliminating indoor air pollutants, allergens, and contaminants. Their operation allows for removing potentially harmful particles from indoor environments, thereby significantly enhancing air quality within enclosed spaces.
The process employed by Energy-Recovery Heat Exchangers is particularly beneficial in environments where maintaining a clean and healthy indoor atmosphere is paramount. Educational institutions, healthcare facilities, and office buildings, where high concentrations of individuals are present, find these systems indispensable in ensuring the well-being and productivity of occupants.
By facilitating a continuous supply of fresh air, these heat exchangers play a pivotal role in preventing the accumulation of pollutants, thus fostering a healthier indoor environment. Moreover, these systems’ ability to transfer heat between incoming and outgoing air streams without mixing them ensures that energy efficiency is not compromised. This attribute is crucial, considering the growing emphasis on reducing energy consumption and minimising environmental impact.
The Environmental and Economic Impact of Adopting Fresh Air Heat Exchanger
Integrating Fresh Air Heat Exchanger within various sectors marks a significant stride towards harmonising environmental conservation with economic pragmatism. These systems, designed to optimise energy use through waste heat recovery, stand at the forefront of efforts to mitigate the adverse effects of climate change. By efficiently utilising the heat from exhaust air to warm or cool incoming fresh air, Fresh Air Heat Exchangers significantly reduce the dependency on fossil fuels, a critical factor in reducing greenhouse gas emissions. This transition to more sustainable energy sources underscores these exchangers’ pivotal role in fostering a greener planet.
On the economic front, deploying Fresh Air Heat Exchangers is synonymous with enhanced cost-efficiency. Industries and residential settings benefit from the lowered energy demands these systems promote, resulting in a noticeable decrease in energy expenditure. This reduction in operational costs is particularly relevant in today’s economic climate, where resource optimization is not just preferred but essential. For businesses, the savings realised by applying these heat exchangers can be redirected towards innovation and growth, thus enhancing competitive advantage.
The deployment of Energy-Recovery Heat Exchangers, whilst replete with advantages, is not without its hurdles. The foremost challenge lies in the financial aspect, with the initial investment often significant. The capital outlay for these systems encompasses not only the heat exchangers’ cost but also the expense of integrating them into existing energy systems, which can be complex and costly. Additionally, there is the aspect of ongoing maintenance, which is vital to ensure the efficient operation of the heat exchangers over time but adds to the total cost of ownership.
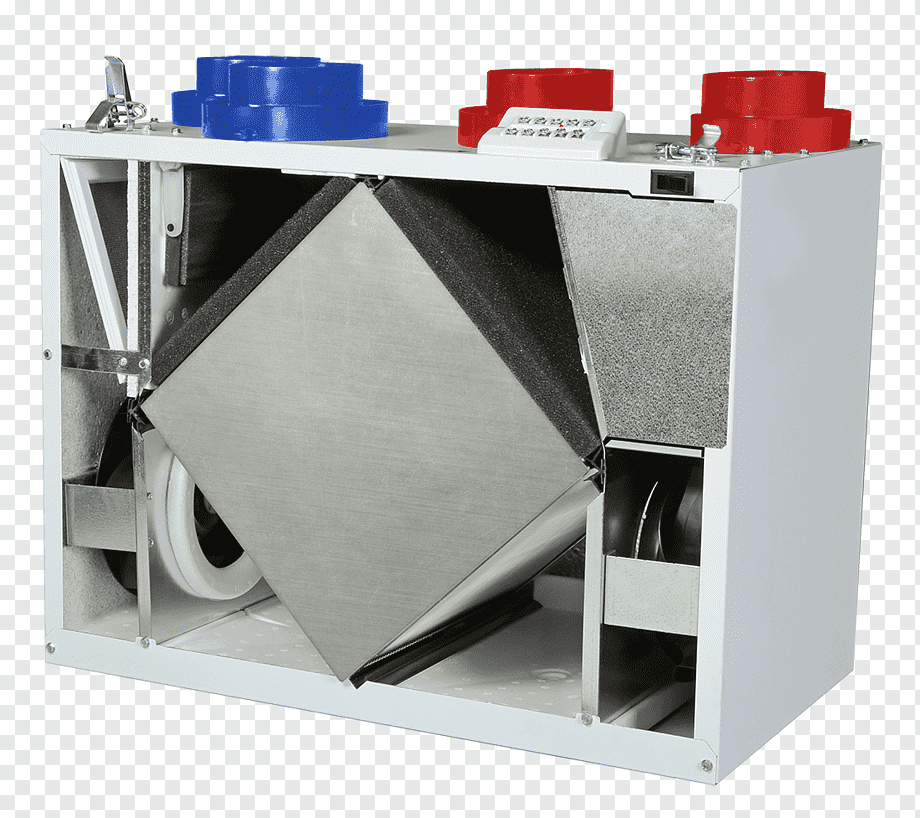 Furthermore, integrating Energy-Recovery Heat Exchangers into existing infrastructures can present technical challenges. These systems must be meticulously designed and configured to match a facility’s specific energy recovery needs whilst seamlessly integrating with its existing HVAC or industrial processes. This requires a high level of technical expertise and often a bespoke solution, which can increase the complexity and cost of projects.
Furthermore, integrating Energy-Recovery Heat Exchangers into existing infrastructures can present technical challenges. These systems must be meticulously designed and configured to match a facility’s specific energy recovery needs whilst seamlessly integrating with its existing HVAC or industrial processes. This requires a high level of technical expertise and often a bespoke solution, which can increase the complexity and cost of projects.
Regulatory compliance also poses a potential challenge. As governments worldwide tighten energy efficiency standards and emissions regulations, systems must be efficient and compliant with current and future legislation. This necessitates a thorough understanding of the regulatory landscape, which can be time-consuming and challenging.
Despite these challenges, the strategic implementation of Energy-Recovery Heat Exchangers, supported by expert planning and execution, promises to unlock significant energy conservation and operational efficiency benefits. Therefore, the journey towards integrating these systems demands careful consideration of both the hurdles and the pathways to overcoming them.
The Future of Energy Efficiency: The Role of Heat Exchanger Vent
In an era where the impetus on energy efficiency and sustainability intensifies, the significance of Heat Exchanger Vent technology in this dialogue cannot be overstated. These systems, which capitalise on the principle of waste heat recovery from ventilation processes, stand at the vanguard of efforts to advance energy optimisation. Adopting Heat Exchanger mechanisms is instrumental in augmenting the overall efficiency of buildings and industrial settings by ensuring minimal energy is wasted, thereby contributing to a reduction in carbon footprints.
The trajectory of energy efficiency is being redefined through the proliferation of these technologies, with Heat Exchanger Vents playing a central role. As advancements in materials science and thermal management strategies evolve, the efficacy and applicability of heat exchanger vents are expected to broaden. This expansion is anticipated to facilitate the integration of these systems across a more diverse array of sectors, offering unprecedented opportunities for energy savings and environmental conservation.
Moreover, the burgeoning awareness among stakeholders about the tangible benefits derived from implementing such technologies is likely to spur increased investment and innovation in the field. The convergence of technological advancement and heightened environmental consciousness heralds a promising horizon for Heat Exchanger technology, solidifying its position as a cornerstone in the quest for a more energy-efficient and sustainable future.
FAQs
What Exactly Is An Energy-Recovery Heat Exchanger?
An Energy-Recovery Heat Exchanger is a device that captures waste heat from one process or environment and uses it to warm or cool another, thus optimising energy usage without the two streams mixing.
How Do Energy-Recovery Heat Exchangers Contribute To Sustainability?
By reclaiming and reusing heat that would otherwise be lost, these systems reduce the need for additional energy sources, conserving energy and decreasing greenhouse gas emissions.
Can Energy-Recovery Heat Exchangers Be Integrated Into Existing Heating And Cooling Systems?
Yes, they are designed to be adaptable and can be retrofitted into existing HVAC systems or other industrial processes to enhance energy efficiency.
What Are The Primary Challenges Of Installing An Energy-Recovery Heat Exchanger?
The initial investment and the need for technical expertise in customising the system to specific requirements are the main hurdles, alongside ensuring compliance with evolving regulatory standards.
Are There Financial Benefits To Implementing An Energy-Recovery Heat Exchanger?
Reducing energy consumption leads to considerable savings on utility bills over time, making it a financially prudent choice in addition to its environmental benefits.
Conclusion
In summarizing the discourse on Energy Recovery Heat Exchanger, it becomes evident that these systems embody the nexus between technological innovation and sustainable development. Through their ability to reclaim and repurpose waste heat, they underscore the potential for significant energy conservation and highlight the shift towards more environmentally responsible practices across industries and residential settings.
| Other Good Articles to Read |
| Blogs Rain |
| Cme Blog Spot |
| Garcias Blogs |
| Yyc Blogs |
| Guiade Blogs |
| Blogs-Hunt |
| Impact-Blog |
| Smarty Blogs |
| Ed Blog |
| Mo Blogs |
| Blogs Em |
| Blogs T |
| Related Business Listings |
| Contact Directory |
| Local Business Profiles |